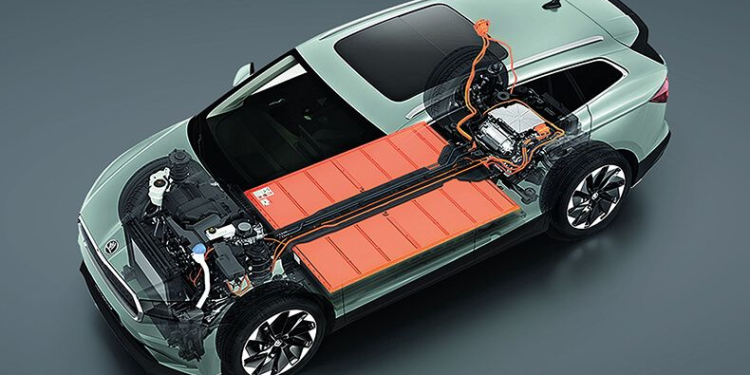
Electric cars are increasingly present on African roads, heralding a new era of sustainable transportation. While these vehicles rely heavily on their high-voltage lithium-ion batteries for propulsion, the traditional 12-volt lead-acid battery remains an essential component. This coexistence between cutting-edge technology and older battery systems is not coincidental but rather a strategic design choice. Here, we explore the reasons behind this dual-battery setup and its importance, particularly in the context of African driving conditions.
Dual Battery System: Propulsion and Powering Equipment
An electric car primarily requires energy for two main functions: propulsion and powering auxiliary equipment. The high-voltage lithium-ion battery, which is both costly and highly efficient, is dedicated to moving the vehicle. However, this battery alone cannot meet all the vehicle’s needs. This is where the 12V battery plays a crucial role. It powers the vehicle’s computers, infotainment systems, lighting, and other electronic accessories, ensuring the smooth operation of these essential components.
Safety Mechanism
One of the most significant roles of the 12V battery is its function in safety mechanisms. It powers the relays that separate the high-voltage battery from the vehicle’s low-voltage systems. In the event of an accident or when the vehicle is stationary, these relays help disconnect the high-voltage system from the rest of the car’s electrical network. This separation is crucial for preventing electric shocks and ensuring the safety of passengers and first responders.
Reliability and Simplicity
The 12V battery is favored for its simplicity and reliability. Manufacturers and suppliers have decades of experience with 12-volt systems, making them cost-effective and easy to produce. For users, this familiarity means that troubleshooting and maintenance are straightforward. For instance, if the 12V battery fails, a simple jump-start using traditional jumper cables can often resolve the issue. This ease of use is particularly beneficial in Africa, where access to advanced repair facilities may be limited.
A spokesperson from Hyundai elaborates on this point, stating that “all of the vehicle’s computers are powered by low voltage, as are the relays that separate power from the high-voltage battery and the rest of the car’s high-voltage network.” This ensures a higher level of security and reliability, making electric vehicles safer and more dependable.
Essential Safeguard
The 12V battery acts as a critical safeguard against electricity-related risks. It ensures that even if the high-voltage system encounters issues, the vehicle can still operate its essential functions safely. This dual-battery system thus provides a robust framework that balances high-tech propulsion needs with practical, reliable power for auxiliary systems.
Conclusion
In summary, the 12V battery in electric cars is indispensable for several reasons: it powers essential equipment, enhances safety through its role in relay operations, and offers a simple, reliable solution for everyday maintenance and troubleshooting. For drivers in Africa, this means a more dependable and safer electric vehicle, capable of navigating diverse and challenging driving conditions.