A guide to essential checks during a car service in South Africa, plus your rights and responsibilities under the Consumer Protection Act.
Car Service Checklist South Africa: Ensuring a Thorough Inspection
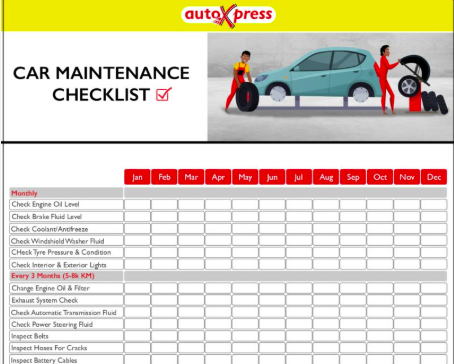
Regular car maintenance is crucial for vehicle longevity and safety, but knowing what to expect during a service can be confusing. This Car Service Checklist South Africa outlines key areas that should be addressed during a routine service, according to the Motor Industry Workshop Association (MIWA), and clarifies your rights as a consumer. It is important to service you car, and make use of preventative steps.
Essential Service Checks
MIWA recommends that the following components be inspected and, if necessary, addressed during a standard car service:
⦁ Engine Oil: Topping up or replacing engine oil is vital for engine health and longevity.
⦁ Fuel Injection System: Cleaning the fuel injection system can restore engine performance and improve fuel efficiency.
⦁ Wheel Alignment: Proper wheel alignment ensures even tire wear, a balanced ride, and better fuel economy.
⦁ Brakes: A thorough brake inspection is critical for safe driving, ensuring the vehicle can stop effectively and immediately.
⦁ Wiper Blades: Checking wiper blades ensures clear visibility during rain or other adverse weather conditions.
⦁ Tire Rotation and Balancing: Rotating and balancing tires promotes even tread wear, extending tire life and providing a smoother ride. This will also help to understand the condition of the tyres.
⦁ Battery: Testing the battery’s ability to hold a charge helps prevent unexpected breakdowns.
While basic car knowledge is helpful, MIWA emphasizes that certain repairs and inspections should be left to qualified technicians at accredited workshops. For additional tips and information about preventative car care, and a variety of other motoring topics you can check reliable resources.
Your Rights Under the Consumer Protection Act
The South African Consumer Protection Act (CPA) provides significant protections for consumers when dealing with car repair and maintenance shops. The Retail Motor Industry Organisation (RMI) highlights key aspects of the CPA:
⦁ Pre-Authorization: A service provider cannot charge for parts, services, maintenance, or repairs without the consumer’s authorization (Section 15 of the CPA).
⦁ Cost Options: Consumers have the right to choose between an estimate, a maximum price limit, or giving the repairer “carte blanche” to complete the work. Once a choice is made, the consumer is liable for the agreed-upon cost.
⦁ Accurate Information: Service providers must provide accurate and truthful information, avoiding false, misleading, or deceptive representations (Section 41 of the CPA).
⦁ Delays and Damages: The workshop must inform the customer in advance of any expected delays. If the workshop negligently or intentionally damages the vehicle, they are responsible for rectifying the damage (Section 54 of the CPA).
⦁ Return of Parts: The service provider is generally required to return old or replaced parts to the consumer (Section 67 of the CPA), except for items replaced under warranty, insurance claims, or those requiring specialized disposal.
⦁ Right to report: If the service is substandard, the consumer can report to the⦁ ⦁ Motor Industry Ombudsman of South Africa (MIOSA)
⦁ Warranty on Repairs: Consumers have a six-month implied warranty on repairs. If the repairs are faulty, the consumer can demand that the supplier either fix the problem or refund the price paid (Section 56 of the CPA).
Understanding these rights and responsibilities empowers consumers to engage confidently with workshops and ensure they receive fair and competent service.
Have you ever had a dispute with a car repair workshop? Share your experience and how you resolved it in the comments!